How Does eSim Work?
An eSIM works by storing your mobile plan as a downloaded digital profile on a tiny chip embedded in your phone instead of a removable plastic SIM. The profile is installed over the internet using a QR code or activation code, then used by your device to authenticate with a mobile network for calls, SMS, and data.csgi+1
What is an eSIM exactly?
An eSIM (embedded SIM) is a rewritable chip (eUICC) soldered onto the device motherboard at the factory. It can hold one or more SIM profiles, each with its own ICCID, IMSI, and authentication keys just like a physical SIM.wikipedia
- Functions identically to a classic SIM from the network’s perspectivewikipedia
- Cannot be physically removed, but profiles can be added, deleted, or replaced via softwarebetterroaming
- Identified by a unique EID (eUICC ID) that carriers use for secure provisioningwikipedia
How does eSIM connect to a mobile network?
An eSIM profile contains the credentials your phone presents to the carrier’s core network to register and attach to data and voice services. The process follows remote SIM provisioning standards from GSMA.wikipedia
- After installation, the profile stores network keys and identifiers, which your device uses during network authenticationcsgi
- The network then authorizes voice, SMS, LTE, 5G, and roaming exactly as with a plastic SIMairalo
- Multiple profiles can exist on a single eSIM, but usually only one is active at a time on most phonesbetterroaming
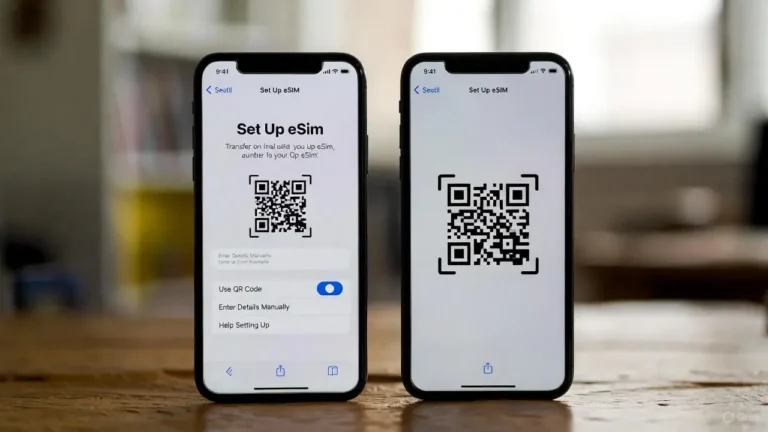
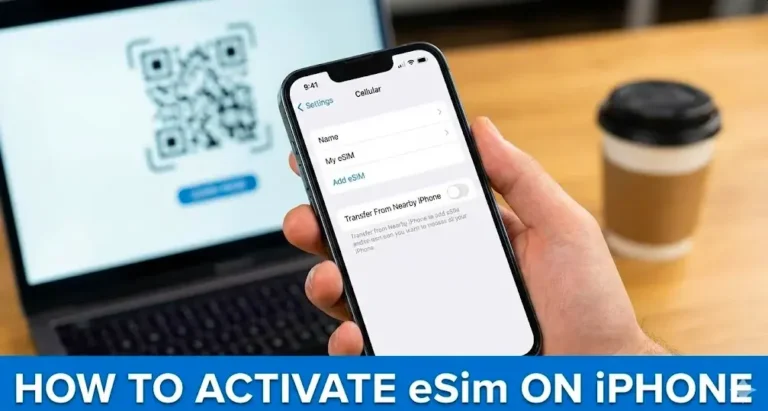
How is an eSIM profile installed?
Instead of inserting a card, the carrier or eSIM app sends a digital profile that your device downloads over WiFi or existing mobile data.airtel+1
- You typically scan a 2D QR code that contains an activation code and server address for the subscription managerairtel
- The phone sets up a secure channel to the remote server, verifies the EID, then downloads and installs the SIM profile to the eUICCwikipedia
- Some operators also support in-app activation or instant “carrier activation” without QR codesairtel
How does switching carriers or plans work?
With eSIM, switching plans is usually software-only, not hardware.airalo
- You can delete the old profile and download a new one from another provider, or store several profiles and switch which is activebetterroaming
- Many travel eSIM apps let you buy a plan, tap “Install eSIM,” and get connected in minutes without visiting a storeairalo
- Devices that support dual eSIM can run two profiles at once, for example “home” and “travel” lineseasysim
What technical standards does eSIM use?
eSIM uses an eUICC chip following GSMA and ISO standards so that networks treat it like a normal SIM but with remote management.wikipedia
- eUICC often uses the MFF2 form factor (about 6 mm × 5 mm) soldered on the boardwikipedia
- Remote provisioning uses GSMA’s RSP architecture, with subscription management servers that securely push profiles using the device’s EIDcsgi+1
- Once installed, profiles behave like standard SIM applications with file systems and security domains defined by 3GPP and ETSIwikipedia
How does eSIM affect tethering and data?
From the phone’s operating system perspective, an eSIM data plan is just another cellular interface.airalo
- Hotspot / tethering works the same way as with a physical SIM, limited only by carrier policy on that specific eSIM planeasysim
- Data speed (LTE, 5G, NR) depends on network technology and spectrum, not on whether the SIM is physical or embeddedairalo
- APN and data settings are usually pushed automatically with the profile, but can sometimes be edited in the device APN menusimology
What security protections does eSIM use?
eSIM adds security by avoiding removable cards and using encrypted provisioning.csgi+1
- The eUICC is a tamper-resistant secure element, similar to a traditional SIMwikipedia
- Profile downloads use mutual authentication between device and subscription server, tied to the EIDwikipedia
- Because the chip cannot be removed, there is lower risk of SIM theft or cloning via card swapping, though account takeover risks remain at the carrier sidecsgi
When does eSIM not work well?
Despite flexibility, eSIM still has practical limitations.airalo+1
- Some carriers or regions do not yet support remote eSIM provisioning or limit eSIM to postpaid lines
- Profiles often cannot be freely moved from one phone to another without carrier assistance and re-provisioningwikipedia
- Older phones or budget models may lack eUICC hardware, so they still rely only on physical SIMsbetterroaming
YouTube explainers worth watching
These videos visually walk through how eSIM works and how profiles are provisioned:
Apple-style overview of eSIM setup and behavior:
General “what is eSIM and how it works” animation:

Tasnima Tabassum Ema is the Founder and Lead Data Analyst at eSIM Expart. Driven by her own costly roaming nightmares, she built the site to save fellow travelers money. She specializes in rigorous, real-world testing and calculating the true cost per Gigabyte ($/GB) to ensure you always get the cheapest, most reliable connection.